QuestSim: Human Motion Tracking from sparse Sensors with Simulated Avatars
SIGGRAPH Asia 2022
[PDF]
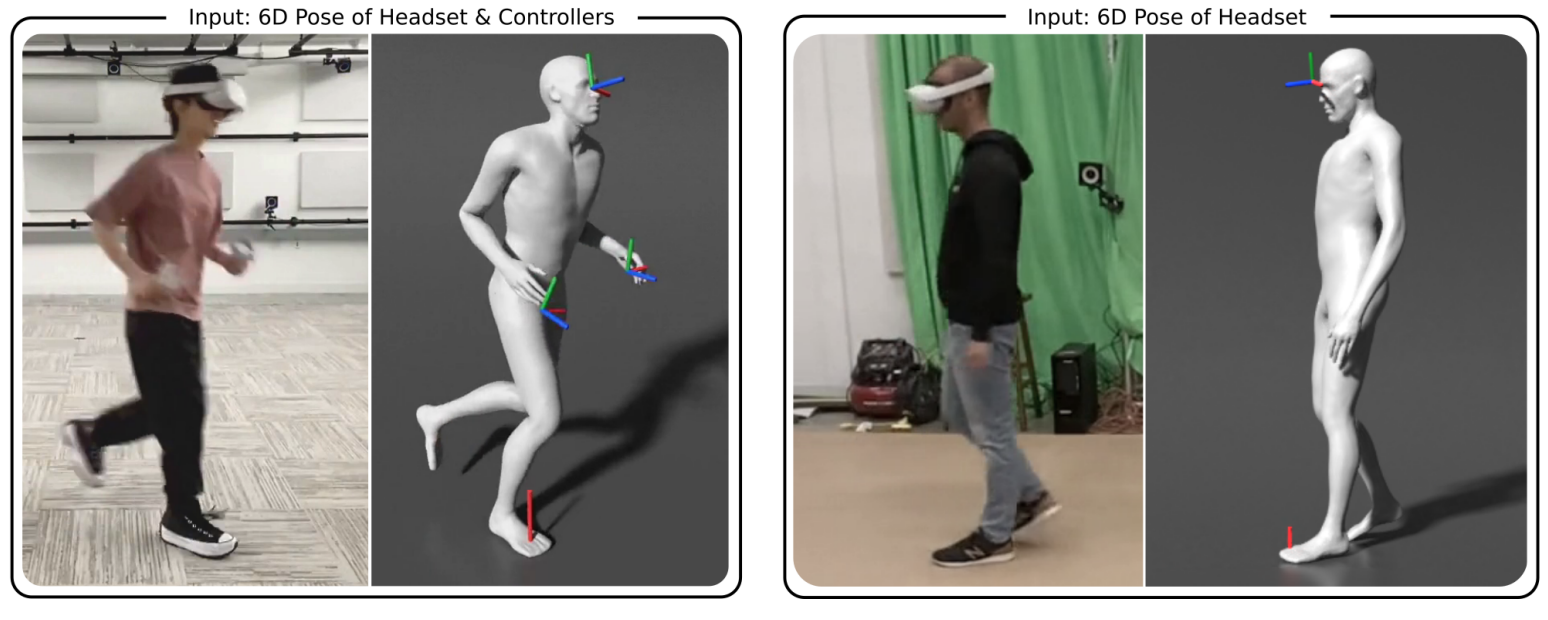
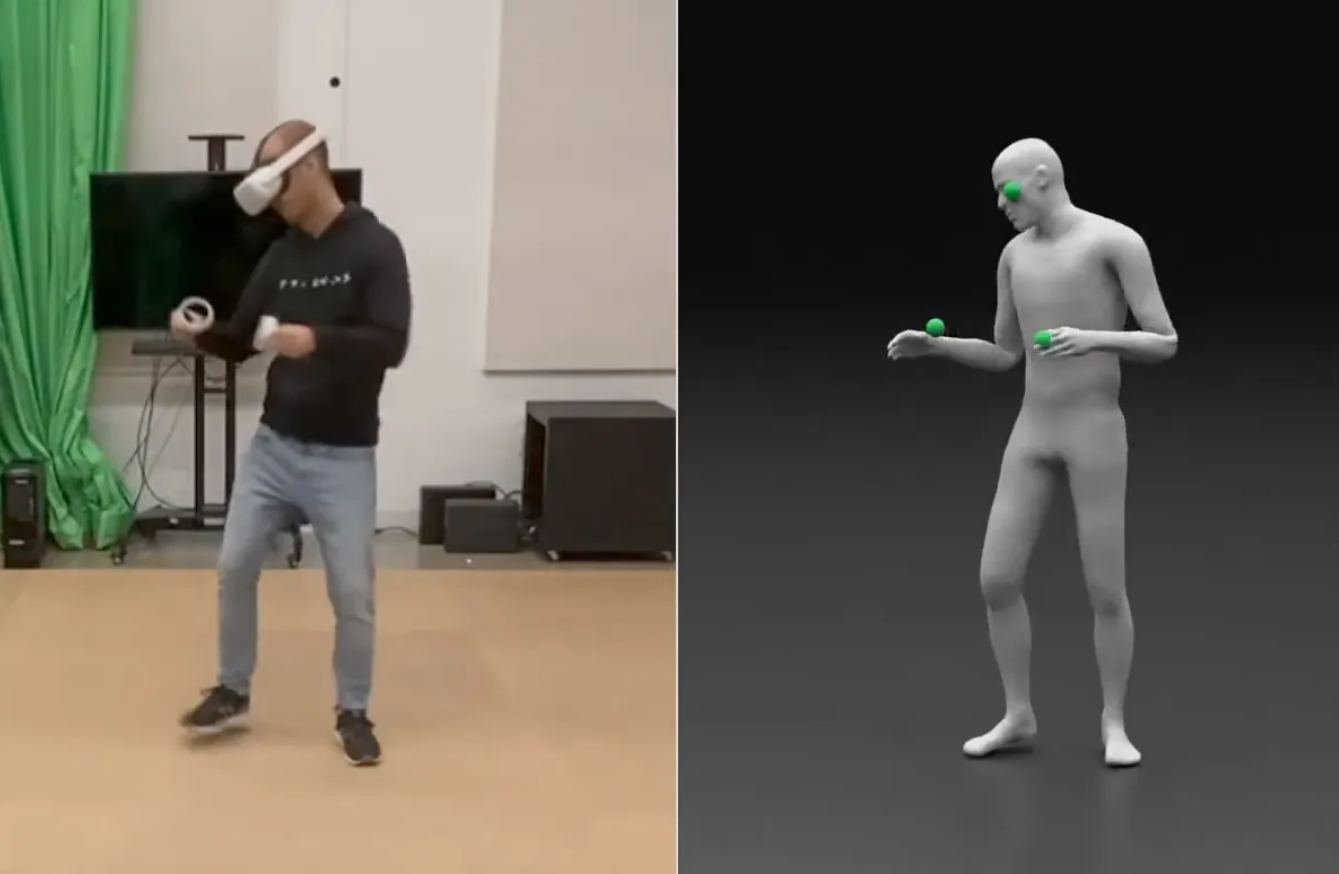
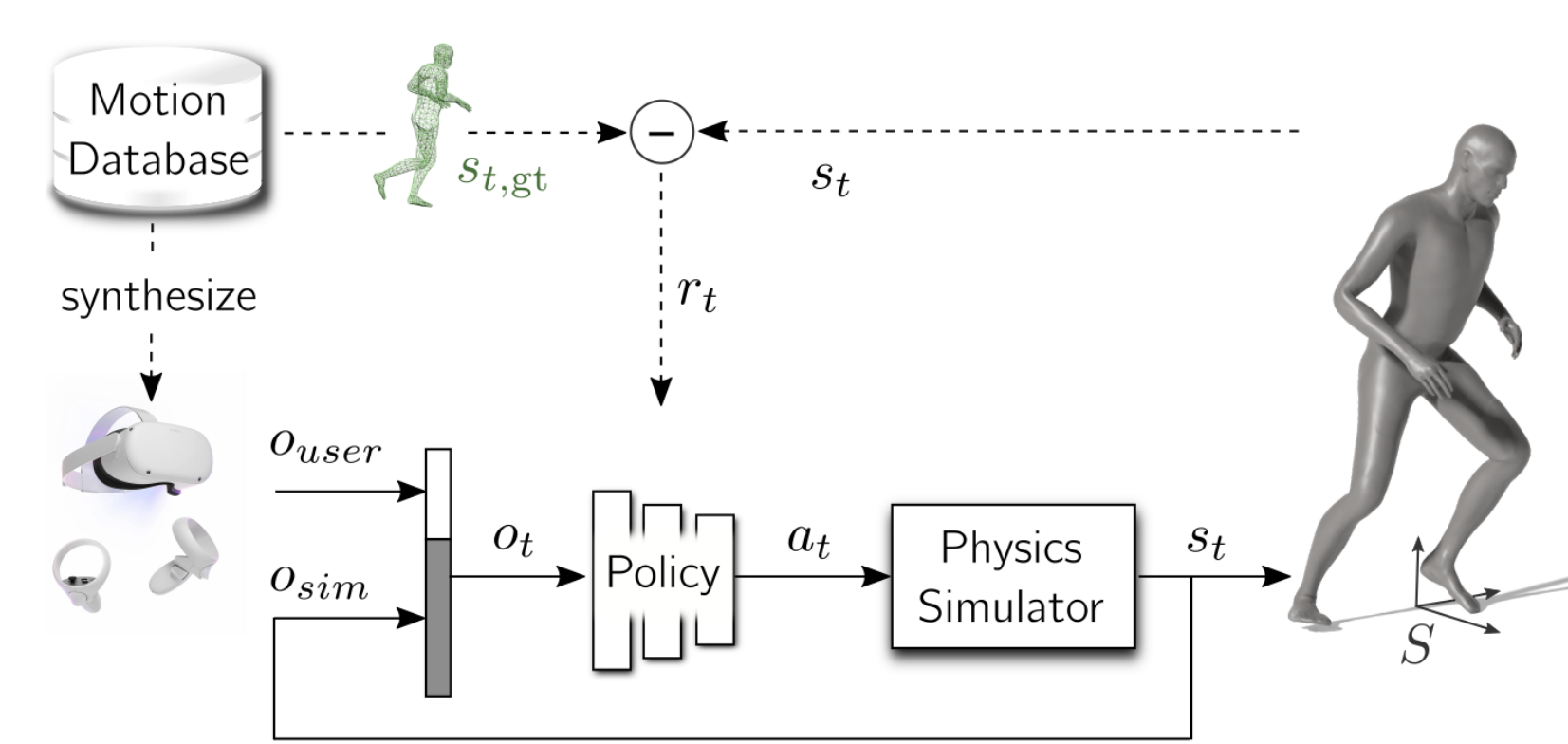
Real-time tracking of human body motion is crucial for interactive and immersive experiences in AR/VR. However, very limited sensor data about the body is available from standalone wearable devices such as HMDs (Head Mounted Devices) or AR glasses. In this work, we present a reinforcement learning framework that takes in sparse signals from an HMD and two controllers, and simulates plausible and physically valid full body motions. Using high quality full body motion as dense supervision during training, a simple policy network can learn to output appropriate torques for the character to balance, walk, and jog, while closely following the input signals. Our results demonstrate surprisingly similar leg motions to ground truth without any observations of the lower body, even when the input is only the 6D transformations of the HMD. We also show that a single policy can be robust to diverse locomotion styles, different body sizes, and novel environments.
Videos
News
This paper shows some of our research at Meta Reality Labs in reconstructing a user's pose from only the sensors of the Quest headset using Reinforcement Learning.
— Alexander Winkler (@awinkler_) September 22, 2022
authors: with Jungdam Won and Yuting Ye
paper: https://t.co/hpZhuY8PC1
video: https://t.co/BBRGMoHt4t
1/4👇 pic.twitter.com/EiwQ54R5th
Bibtex
@inproceedings{10.1145/3550469.3555411,
author = {Winkler, Alexander and Won, Jungdam and Ye, Yuting},
title = {QuestSim: Human Motion Tracking from Sparse Sensors with Simulated Avatars},
year = {2022},
doi = {10.1145/3550469.3555411},
booktitle = {SIGGRAPH Asia 2022 Conference Papers},
location = {Daegu, Republic of Korea},
}
